Pharmacological procedures for creation of a new drug
1. Identification of disease mechanisms and targetsRelevant expertise: PharmacologyWhat are targets? What is the relationship between targets and new drugs?Generally, once a new target for drug action is discovered, it often becomes a breakthrough for a series of new drug discoveries.In simple terms, if we compare the disease to a lock, then the target is the lock core. Once we find the lock core and study its three-dimensional structure, we can develop a proprietary key based on its structure. The new drug is like this proprietary key.
2. Computer-aided identification of lead compoundsRelevant expertise: Medicinal chemistryLead compound: After the target is identified, the spatial structure of the target is simulated using a computer. Different lead compounds have different spatial structures, so the computer is used to fit the target and the spatial structure.Concept of lead compound: Also known as a lead, it is a compound with certain biological activity and chemical structure obtained through various methods and means and is used for further structural modification and optimization. It is the starting point for modern new drug research.Based on the identified target, the 3D structure of the target is depicted by using a computer, and various compound structures are fitted to it so as to find the corresponding lead compound.
3. Synthesis of lead compoundsRelevant expertise: Medicinal chemistryAfter obtaining the spatial structure of the lead compound through computer-aided design, a synthesis route for the lead compound is designed and the lead compound is synthesized in the laboratory.
4. Determination of the structure of lead compoundsRelevant expertise: Pharmaceutical analysisAfter the synthesis of the lead compound is completed, we need to examine its structure using techniques such as mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.


5. In vitro pharmacological testsRelevant expertise: PharmacologyAfter determining the synthesized compound's structure, a series of in vitro pharmacological tests (cell experiments) are conducted to preliminarily verify the drug's efficacy.
6. Optimization of lead compoundsRelevant expertise: Medicinal chemistryDue to certain deficiencies in lead compounds, such as insufficient activity, chemical instability, high toxicity, poor selectivity and unreasonable pharmacokinetic properties, the lead compounds need to be chemically modified and further optimized to develop ideal target compounds.

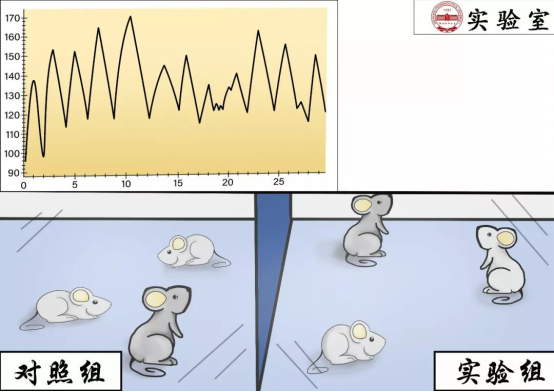
7. In vivo experimentsRelevant expertise: PharmacologyAfter passing in vitro pharmacological tests, further in vivo experiments are conducted to validate the drug's efficacy. Animal metabolites are obtained for pharmacokinetic studies.
8. Analysis of metabolitesRelevant expertise: Pharmaceutical analysisAnimal metabolites and excreta are subjected to a series of sample preparation processes to obtain a test solution. Techniques such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry are used for analysis.

9. Drug formulationRelevant expertise: Pharmaceutical formulationDrug formulation is to conduct research on which dosage form of the drug has a more significant therapeutic effect. For example, drugs encapsulated in capsules are usually powders or granules that are irritating to the esophageal and gastric mucosa. Some drugs are easily volatile or easily degraded by saliva in the oral cavity, while special film-coated capsules made of special film-forming materials can protect drugs from being destroyed by gastric acid, avoiding drug loss, waste and reduced efficacy.

10. Drug analysisRelevant expertise: Pharmaceutical analysisAfter the formulation research is completed, the drug needs to undergo impurity testing and the impurity content limits need to comply with pharmacopoeia requirements.

11. Clinical trialsRelevant expertise: Clinical pharmacyClinical trials refer to systematic studies of drugs conducted in human subjects (patients or healthy volunteers) to confirm or reveal the drug's effects, adverse reactions, and/or drug absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion. The purpose is to determine the drug's efficacy and safety.Clinical pharmacy is mainly responsible for studying the theory and methods of achieving the highest efficacy of drugs in the human body's metabolic process. It focuses on the relationship between drugs and humans, directly involving the drug itself, the target population and the administration method, thus directly impacting healthcare quality.

12. Drug registration and applicationRelevant expertise: Drug administration managementBased on the application of the drug registration applicant, the National Medical Products Administration evaluates the safety, efficacy and quality controllability of the drug to be marketed in accordance with the statutory procedures and decides whether to approve the application or not.

13. Bulk production of drugs

14. Drug marketing


